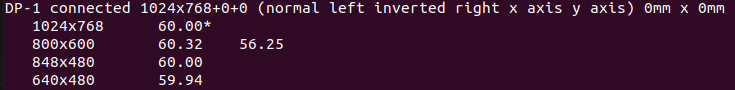
- Find the monitor or display using the xrandr command
$xrandrHere, DP-1 will be your Display / Monitor ID
2. Get the Modeline string using one of below command
cvt 1366 768or
gtf 1920 1080 60
3. Add new mode using Modeline output
xrandr --newmode "1920x1080_60.00" 172.80 1920 2040 2248 2576 1080 1081 1084 1118 -HSync +Vsync4. Add created new mode to desired display
xrandr --addmode DP-1 "1920x1080_60.00"Once this is done you can see the Resolution in the Settings > Display > Resolution dropdown.

5. Add to your bash profile to make it permanent
sudo gedit ~/.profileAdd below two commands to there.
xrandr --newmode "1920x1080_60.00" 172.80 1920 2040 2248 2576 1080 1081 1084 1118 -HSync +Vsync
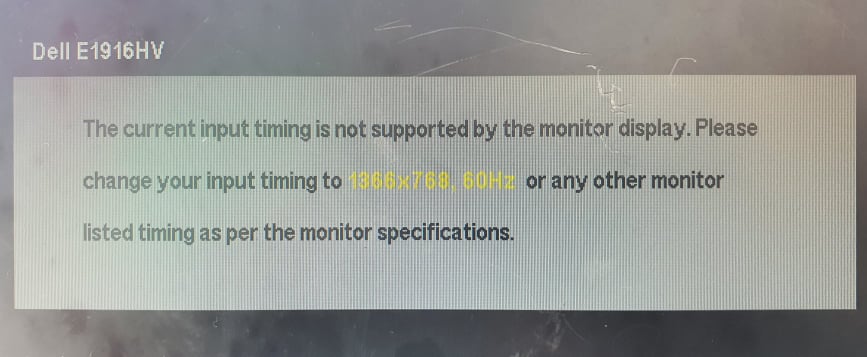
xrandr --addmode DP-1 "1920x1080_60.00"Note : Check the maximum resolution that monitor supports also otherwise it will display something like this.
References :
- https://blog.mohessaid.com/fix-external-monitor-resolution-in-ubuntu-20-04-9c24cee65950
- https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/227876/how-to-set-custom-resolution-using-xrandr-when-the-resolution-is-not-available-i
- https://askubuntu.com/questions/138408/how-to-add-display-resolution-for-an-lcd-in-ubuntu-12-04-xrandr-problem